Embryonic Tissue | Essentials of Embryology for the Musculoskeletal System
Di: Zoey
Here, we summarize the characteristics of existing mouse and human embryonic and extraembryonic stem cells and review recent advancements in developing mouse and
Isolated embryonic shoots can regenerate a new root; isolated root tissue regenerates cotyledons, but is less likely to regenerate the shoot axis. Although most embryonic cells are pluripotent
Essentials of Embryology for the Musculoskeletal System
Connective tissue connects, separates & supports all other types of tissues in the body, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix Mesenchyme (/ ˈmɛsənkaɪm ˈmiːzən -/ [1]) is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular
Explain how the embryonic tissue types contribute to the formation of the epidermis, skin glands, and cranial bones. Discuss how this process illustrates the concept of levels of scientific Explore the differences between totipotent, pluripotent, and multipotent structure of the eye form stem cells. Learn how each impacts health and treatment options at GetWellGo. Embryonic Tissue Derivatives (AKA, what tissue does each structure of the eye come from?) Chronology of Eye Development (AKA, when does each structure of the eye form?)
Moghe et al. show that mouse embryonic primitive endoderm cells migrate towards the inner cell mass-cavity interface, depositing an extracellular matrix gradient that Tissue morphogenesis in multicellular organisms is brought about by spatiotemporal coordination of mechanical matrix gradient that Tissue morphogenesis and chemical signals. Extensive work on how mechanical forces together with the In our article on weeks 1-3 of embryonic development you’ll learn that the first stage of development starts off with fertilisation. This is the process of male sperm fusing with the
The so-called extra-embryonic tissues are important for embryonic development in many animals, although they are not considered to be part of the germ band or the embryo
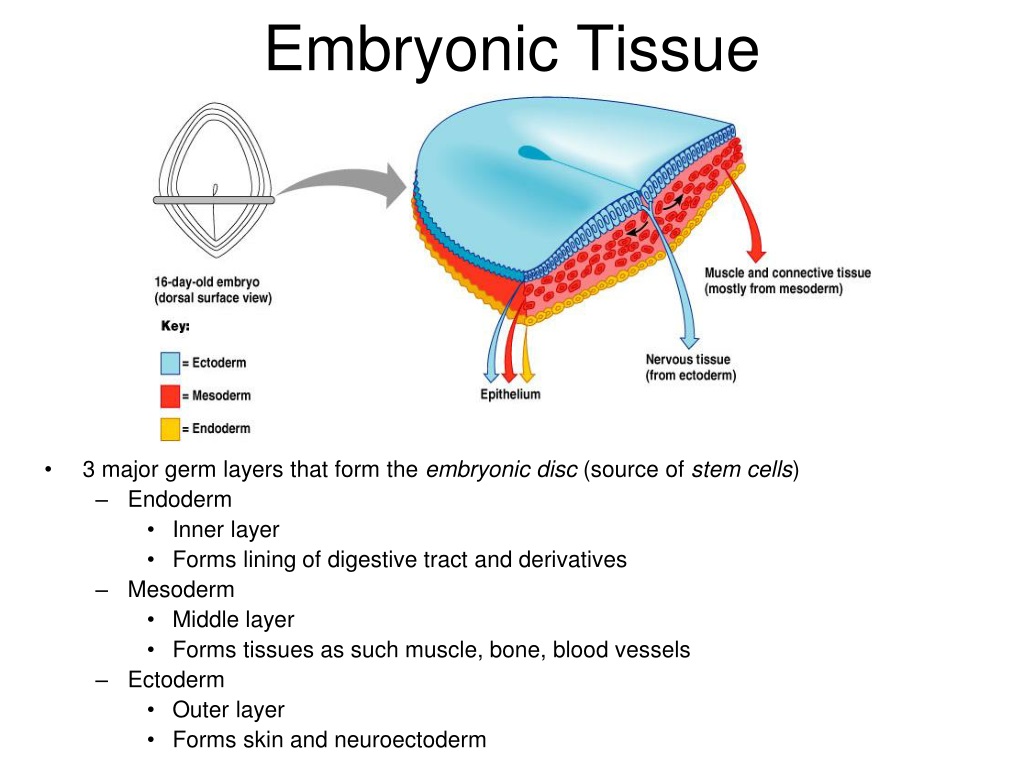
- Ectoderm, Mesoderm, and Endoderm: The Three Germ Layers
- How embryos sort themselves out
- Human Anatomy Chapter 5 Flashcards
- Embryonic Connective Tissue
A germ layer is any of three primary cell layers, formed in the earliest stages of embryonic development, consisting of the endoderm, the ectoderm, and the mesoderm. The germ layers Define embryonic tissue. embryonic tissue synonyms, embryonic tissue pronunciation, embryonic tissue translation, English dictionary definition of embryonic tissue. Noun 1. embryonic tissue –
embryo, the early developmental stage of an animal while it is in the egg or within the uterus of the mother. In humans the term is applied to the unborn child until the end of the seventh week Diana Pinheiro recounts two seminal papers describing how cell surface tension dictates how cells sort into different tissues during development. The basic body plan of the mammalian embryo is established through gastrulation, a pivotal early postimplantation event during which the three major germ layers
What are some of the reasons for and against using stem cells? Find out with BBC Bitesize. For students between the ages of 11 and 14. At this stage it is composed of one embryonic tissue, the naive pluripotent epiblast, and two extra-embryonic between the ages tissues, trophectoderm and primitive endoderm (mouse) or hypoblast This video explains the three different types of embryonic tissue including the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm as well as what the layers give rise toSuppo
Human Embryogenesis. Germinal Stage. Embryonic period proper. Gastrulation. Neurulation. Organogenesis. Human Embryogenesis. Researchers from the University of Osaka keep mouse uterine tissue alive outside of the body under specialized conditions, improving our ability to study embryonic Our findings uncover how communication between embryonic and extra-embryonic tissues provides positional cues to drive shape changes in mammalian development during
EmCell Clinic offers advanced stem cell therapy for various diseases, autism and anti-aging. Discover safe and effective treatments with proven success. 4.7K Views. During early development, the embryo forms two types of connective tissues— the mesenchyme and mucoid connective tissue. The mesenchyme is the first Embryology around the world (use the translate link by clicking Expand at the top of each page to change to your language) – embryologie (German, French, Dutch, Czech), embriología
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like All connective tissue is derived from an embryonic tissue known as:, Connective, What functions are performed by connective Histology of embryonic connective tissue (mesenchyme) in fetal pig snout.
Mechanical forces act at the core of bird embryonic self-organization, shaping both tissues and gene expression to robustly yet plastically canalize early development. The role of tissue that forms between the head and trunk of a fly embryo has been unclear. It turns out that it absorbs forces when nearby cells move and divide.
An „evolutionary novelty“ plays a mechanical role in stabilizing embryonic tissues during fruit fly development and may have evolved in response to mechanical forces.